Structuring the API
Kleuth uses the directory tree to map requests to handler functions. To create REST API routes, simply create a directory structure that mirrors the expected routing of the API.
These docs use the example below, where kleuth.core.pathToRoot has been set to io/alienhead/pizza_restaurant/api/rest.
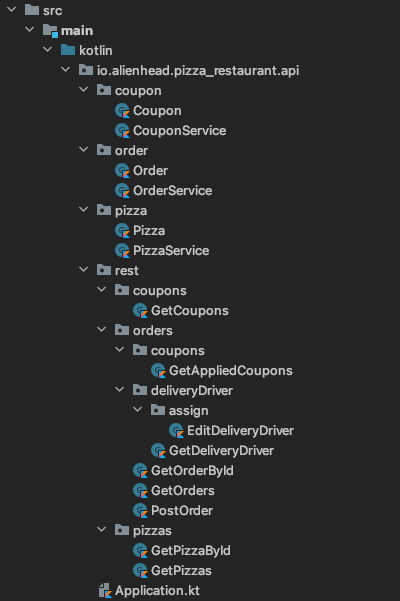
Defining the API#
A url path segment is defined by creating a directory.
The pizzas directory in the example corresponds to the url /pizzas.
Request Handler classes are created inside those directories to handle specific request methods at that route. The GetPizzas class handles GET requests to /pizzas.
Hyphens#
If there are multiple words in a path segment, it is conventional to separate them with hyphens (-).
Kotlin and Java do not allow for hyphens in package names.
Use camel case in a directory name and Kleuth will convert it to hyphenated (also known as kebab case).
In the example, the directory deliveryDriver will be converted to delivery-driver.
Overriding the Path#
If for some reason the directory structure cannot match the REST API, the path can be manually set in the request handler class.
Full Example#
The example directory structure would map to the following REST API
(POST /orders/{id}/delivery-driver/assign and PUT /orders/{id}/delivery-driver/assign are both defined in the EditDeliveryDriver class.)