Handling Requests
Route handler classes can be created in a few ways, depending on preferred style.
Route#
Route is the standard annotation that tells Kleuth a class handles one or more request methods.
Classes with this annotation should have unique names GetPizzas, GetOrders, etc.
Classes with @Route are also annotated with the Spring RestController annotation, allowing for backwards compatibility with Spring RestController features.
A class using the Route annotation would look like this:
RequestMethod#
Classes can instead be annotated with RequestMethod to set a request method of the handler as the class name.
RequestMethod must be used along with the Spring RestController annotation.
:
This style can make the directory structure even more concise:
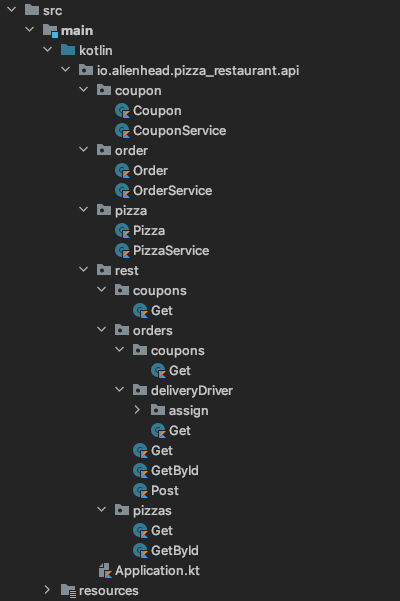
Request Method Handler Functions#
A RequestMethod or Route class may handle one, or many request methods with several options for style.
These functions act just like Spring RequestMapping functions,
allowing the use of Spring function parameter annotations like @PathVariable, RequestBody, Valid, and RequestParam, to name a few.
This also means parameters like Authentication are supported.
Handler#
The word handler is a reserved function name which tells Kleuth the class has one request method handler.
In this case, the class name should start or end with the request method handled by the function.
Using the pizza api example, the class to handle GET /pizzas would look like this:
Request Method as Function Name#
The request method handler function can be named after one of the supported request methods (get, post, put, delete):
This style may be used to put more than one request method in one class:
Request Method as Annotation#
Using the request method annotations can free up the function name to be more specific:
This style may be used to put more than one request method in one class:
note
Since one of Kleuth's goals is to de-obfuscate the REST API structure, including more than one handler function per class may not always be ideal.
Overridding the Path#
It is possible to override the dynamic path Kleuth would create. This is useful if the path does not match the directory structure, but should be used only when necessary.
Simply pass the override path into the RequestMethod or Route annotation:
The path string should be formatted as one would format a Spring RequestMapping path.
note
All route handler classes nested under the route handler with the overridden path must also manually set their path