Setup
Add the Kleuth dependency to your project#
Gradle:#
Optional: Enable Kleuth on the Application class#
Kleuth will autoconfigure by default, but you can also manually add the annotation @EnableKleuth to the main Application class.
Set the necessary application properties#
Kleuth needs to know the fully qualified path to the root of the REST API.
This is set with the kleuth.core.pathToRoot property.
Example#
With the following directory structure:
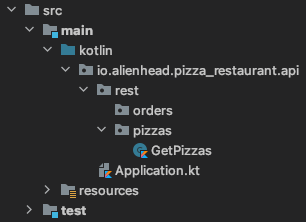
The user expects a GET /pizzas endpoint off the root of the REST API.
Therefore, kleuth.core.pathToRoot should be set like this:
If running locally, the GET pizzas endpoint would be served at localhost:8080/pizzas.
If the pathToRoot property were to be set as follows:
The GET pizzas endpoint would be served at localhost:8080 and the orders package would be ignored.
That's it!#
With @EnableKleuth and the pathToRoot property set, you are ready to dynamically build your Spring REST API with Kleuth!